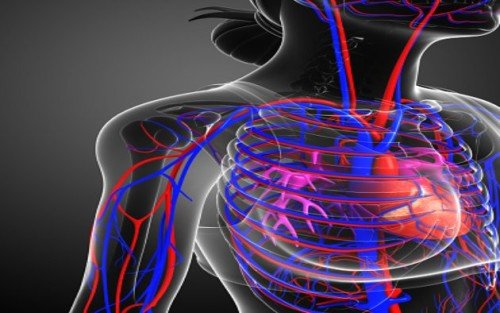
The circulatory system is responsible for the transportation of blood, oxygen, and nutrients to different parts of the body. It consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. Diseases of the circulatory system can affect any of these components, leading to serious health issues. In this blog post, we will discuss some of the common diseases of the circulatory system and their causes.
-
Hypertension: Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common condition in which the force of blood against the walls of the blood vessels is consistently too high. This can lead to damage to the blood vessels, as well as to the heart and other organs. Some of the causes of hypertension include obesity, smoking, stress, and a diet high in salt.
-
Coronary artery disease: Coronary artery disease occurs when the blood vessels that supply the heart become narrowed or blocked, leading to reduced blood flow to the heart. This can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, and even heart attacks. The main cause of coronary artery disease is the buildup of plaque in the arteries, which can be caused by a diet high in cholesterol and saturated fat, smoking, and lack of exercise.
-
Heart failure: Heart failure occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. This can be caused by damage to the heart muscle from coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, or other factors. Symptoms of heart failure include shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling in the legs and feet.
-
Stroke: A stroke occurs when the blood supply to the brain is disrupted, either by a blocked or burst blood vessel. This can cause brain damage, leading to a range of symptoms such as difficulty speaking, paralysis, and loss of vision. The main causes of stroke include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, and heart disease.
Stroke is a serious medical condition that occurs when blood flow to the brain is disrupted, either due to a blockage or a burst blood vessel. This leads to a lack of oxygen and nutrients in the affected area of the brain, causing brain cells to die. Stroke is a leading cause of disability and death worldwide, and prompt recognition and treatment are crucial for the best possible outcome. In this blog post, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatments of stroke.
There are two main types of stroke: ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke. Ischemic stroke occurs when a blood clot blocks a blood vessel in the brain, while hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel ruptures and bleeds into the brain. Both types of stroke can cause serious damage to the brain and can lead to long-term disability or death.
The symptoms of stroke can vary depending on the location and severity of the brain damage. Common symptoms of stroke include sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body; sudden confusion or difficulty speaking or understanding speech; sudden difficulty seeing in one or both eyes; sudden severe headache with no known cause; and difficulty walking, dizziness, or loss of balance or coordination.
If you or someone you know is experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to call emergency services immediately. Every minute counts when it comes to stroke, and prompt treatment can help minimize brain damage and improve outcomes.
Treatment for stroke typically involves a combination of medication, surgery, and rehabilitation. Medications such as clot-busting drugs or anticoagulants may be used to dissolve or prevent blood clots, while surgery may be necessary to remove a blood clot or repair a ruptured blood vessel. Rehabilitation, including physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy, can help individuals regain function and independence after a stroke.
Prevention is also an important aspect of stroke management. Risk factors for stroke include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, high cholesterol, obesity, and a family history of stroke. Lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, exercising regularly, following a healthy diet, and controlling other medical conditions can help reduce the risk of stroke.
Stroke is a serious and potentially life-threatening medical condition that requires prompt recognition and treatment. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of stroke, call emergency services immediately. With early treatment and proper care, many individuals can recover from stroke and regain function and independence.
-
Peripheral artery disease: Peripheral artery disease occurs when the blood vessels outside of the heart and brain become narrowed or blocked. This can lead to reduced blood flow to the limbs, causing pain and numbness. The main cause of peripheral artery disease is a buildup of plaque in the arteries, which can be caused by smoking, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a common circulatory condition in which narrowed or blocked blood vessels reduce blood flow to the limbs, usually the legs. The most common cause of PAD is atherosclerosis, a buildup of plaque in the arteries that carry blood to the legs and feet. This condition can cause pain and numbness in the legs, making it difficult to walk or perform other physical activities.
The symptoms of PAD can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Some people with PAD may not have any symptoms, while others may experience pain or cramping in the legs during physical activity, which goes away with rest. In severe cases, PAD can cause wounds or sores on the legs or feet that don't heal, and can even lead to gangrene or limb amputation.
There are several risk factors for developing PAD, including smoking, diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, obesity, and a family history of PAD. Aging is also a risk factor, as the arteries naturally become stiffer and narrower as we age.
Diagnosis of PAD typically involves a physical exam, review of medical history, and tests such as ankle-brachial index (ABI) and ultrasound. Treatment options for PAD include lifestyle changes, medications, and in some cases, surgery. Lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and following a healthy diet can help manage PAD symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. Medications such as antiplatelet drugs and cholesterol-lowering drugs may also be prescribed. In severe cases, surgical procedures such as angioplasty or bypass surgery may be necessary to restore blood flow to the affected limb.
Overall, PAD is a serious condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications. If you are experiencing symptoms of PAD or have risk factors for the condition, speak with your healthcare provider for evaluation and guidance.
In conclusion, diseases of the circulatory system can have serious consequences for our health and wellbeing. Fortunately, many of these diseases can be prevented or managed through lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking. If you have concerns about your circulatory health, speak to your healthcare provider for advice and guidance.