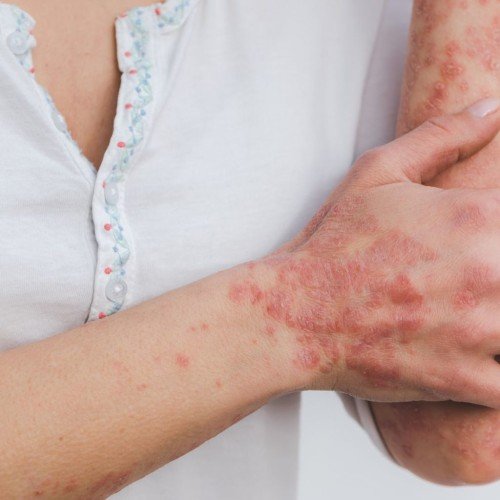
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by red, scaly, and itchy patches on the skin that can be painful and uncomfortable. While the exact causes of psoriasis are not fully understood, it is believed to be related to an immune system problem. This condition is not contagious, but it can be debilitating and affect a person’s quality of life. In this blog post, we will explore the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for psoriasis.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
The symptoms of psoriasis can vary from person to person, but there are some common signs that are usually associated with this condition. The most common symptoms of psoriasis include:
-
Red, scaly patches on the skin: These patches are usually raised and may be covered with a silvery-white buildup of dead skin cells.
-
Itching and burning: Psoriasis can be itchy and uncomfortable, and many people find that the itching and burning are worse at night.
-
Painful, swollen joints: In some cases, psoriasis can also cause joint pain and swelling, especially in the fingers and toes. This is known as psoriatic arthritis.
-
Nails changes: Psoriasis can also affect the nails, causing them to become brittle, discolored, and separated from the nail bed.
-
Thickened skin: Over time, the skin in affected areas can become thickened and develop deep cracks.
Causes of Psoriasis
The exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to an immune system problem. Specifically, it is thought that psoriasis occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. This leads to the production of new skin cells at an accelerated rate, causing the red, scaly patches that are characteristic of this condition.
There are also several other factors that may contribute to the development of psoriasis, including:
-
Genetics: Psoriasis tends to run in families, and it is believed that genetic factors play a role in the development of this condition.
-
Environmental triggers: Certain environmental triggers, such as stress, infections, and changes in the weather, can cause psoriasis to flare up.
-
Medications: Some medications, such as lithium and beta-blockers, can also trigger psoriasis or make it worse.
Treatment Options for Psoriasis
There is no cure for psoriasis, but there are many treatment options available that can help manage the symptoms and improve the appearance of affected skin. The most common treatments for psoriasis include:
-
Topical treatments: Topical creams, ointments, and gels can be applied directly to the skin to reduce inflammation, relieve itching and burning, and improve the appearance of psoriasis lesions. Some common topical treatments for psoriasis include corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and vitamin D analogues.
-
Light therapy: Light therapy, also known as phototherapy, involves exposing the skin to controlled doses of ultraviolet (UV) light. This can help reduce inflammation and slow the production of new skin cells.
-
Systemic medications: In some cases, systemic medications may be needed to manage the symptoms of psoriasis. These medications, which are taken orally or by injection, can help reduce inflammation and slow the production of new skin cells. Some common systemic medications for psoriasis include methotrexate, cyclosporine.
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the skin. It is characterized by red, scaly patches of skin that can be itchy and painful. The exact cause of psoriasis is not known, but it is thought to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some of the most commonly cited causes and triggers of psoriasis include:
-
Genetics: Psoriasis is a genetic condition, meaning that it can run in families. People who have a family history of psoriasis are more likely to develop the condition themselves.
-
Immune system dysfunction: Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition, meaning that the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. This leads to an overproduction of skin cells and the development of psoriatic plaques.
-
Stress: Stress can trigger psoriasis flare-ups or make existing symptoms worse.
-
Infections: Certain infections, such as streptococcal throat infections, can trigger psoriasis in some people.
-
Medications: Certain medications, such as lithium, beta-blockers, and antimalarials, have been known to trigger psoriasis or make existing symptoms worse.
-
Environmental factors: Exposure to certain environmental factors, such as cold weather, trauma to the skin (such as cuts or bruises), and changes in humidity, can trigger psoriasis or make existing symptoms worse.
It is important to note that different people may experience different triggers, and what may trigger psoriasis in one person may not trigger it in another. Additionally, not everyone with psoriasis will experience triggers.