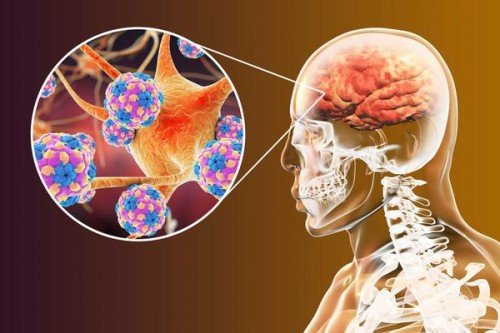
Neurodegenerative diseases are a group of disorders that affect the brain and nervous system, causing a gradual and progressive decline in the normal functioning of these organs. These diseases are caused by the death of neurons in the brain, which results in a range of symptoms that worsen over time. Some common neurodegenerative diseases include Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). In this blog post, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatments of these diseases in more detail.
Causes of Neurodegenerative Diseases
The causes of neurodegenerative diseases are not fully understood, but researchers have identified several risk factors that may contribute to their development. These include genetic factors, age, environmental factors, and lifestyle factors.
Genetic factors play a significant role in many neurodegenerative diseases, such as Huntington's disease, which is caused by a genetic mutation that leads to the death of neurons in the brain. Similarly, Alzheimer's disease has been linked to mutations in several genes, including the amyloid precursor protein (APP) and presenilin genes. Parkinson's disease has also been linked to several genetic mutations, including mutations in the LRRK2 and PARKIN genes.
Age is another significant risk factor for neurodegenerative diseases, as these diseases typically affect older individuals. As people age, their brains become more susceptible to damage, which may contribute to the development of neurodegenerative diseases.
Environmental factors may also play a role in the development of neurodegenerative diseases. Exposure to toxins such as pesticides and heavy metals has been linked to an increased risk of developing Parkinson's disease. Similarly, head injuries have been linked to an increased risk of developing Alzheimer's disease.
Lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise may also contribute to the development of neurodegenerative diseases. A diet high in saturated fats and low in fruits and vegetables has been linked to an increased risk of Alzheimer's disease. Lack of exercise has also been linked to an increased risk of developing neurodegenerative diseases.
Symptoms of Neurodegenerative Diseases
The symptoms of neurodegenerative diseases vary depending on the type of disease and the stage of the disease. Some common symptoms include:
-
Memory loss: Memory loss is a common symptom of Alzheimer's disease, which affects the hippocampus, the part of the brain responsible for memory.
-
Tremors: Tremors are a common symptom of Parkinson's disease, which affects the part of the brain responsible for movement.
-
Muscle weakness: Muscle weakness is a common symptom of ALS, which affects the motor neurons that control voluntary muscle movement.
-
Behavioral changes: Behavioral changes, such as aggression and depression, are common symptoms of Huntington's disease, which affects the part of the brain responsible for mood regulation.
Other common symptoms of neurodegenerative diseases include difficulty speaking, difficulty swallowing, and difficulty walking.
Treatments for Neurodegenerative Diseases
There is currently no cure for neurodegenerative diseases, but there are several treatments available that can help manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. These treatments include medications, therapy, and lifestyle changes.
Medications are commonly used to treat neurodegenerative diseases, such as cholinesterase inhibitors, which are used to treat the cognitive symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. Levodopa is a medication commonly used to treat the motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
Therapy can also be helpful in managing the symptoms of neurodegenerative diseases. For example, speech therapy can help individuals with ALS maintain their ability to communicate, while physical therapy can help individuals with Parkinson's disease maintain their ability to move.
Alzheimer's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is the most common cause of dementia in older adults, with an estimated 6.2 million Americans aged 65 and older living with the disease in 2021, according to the Alzheimer's Association. In this blog post, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Causes of Alzheimer's Disease: Alzheimer's disease is a complex disorder, and the exact causes are not yet fully understood. However, researchers believe that a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors may contribute to the development of the disease. The main risk factor for Alzheimer's disease is age. The risk of developing the disease doubles every five years after the age of 65. Other risk factors include a family history of the disease, genetics, and head injuries.
Symptoms of Alzheimer's Disease: The symptoms of Alzheimer's disease typically begin with mild forgetfulness and can progress to severe cognitive impairment. The most common symptoms of Alzheimer's disease include:
- Memory loss: A person with Alzheimer's disease may forget recently learned information or important dates and events.
- Difficulty with familiar tasks: A person may have trouble with everyday tasks, such as cooking, cleaning, or driving.
- Problems with communication: A person may have difficulty finding the right words or understanding what others are saying.
- Disorientation: A person may get lost in familiar places or have trouble understanding the time or date.
- Changes in mood and behavior: A person may become anxious, agitated, or depressed, or may withdraw from social situations.
Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease: Diagnosing Alzheimer's disease is a complex process that involves ruling out other possible causes of cognitive impairment. A doctor will typically begin by conducting a physical exam and reviewing the patient's medical history. They may also perform tests to assess memory, problem-solving, and other cognitive functions. Imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans, can help rule out other causes of cognitive impairment.
Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease: While there is no cure for Alzheimer's disease, there are treatments available that can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life. The most common treatments for Alzheimer's disease include:
- Medications: Several medications are available to treat the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. These medications work by increasing the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain, which can improve cognitive function and reduce symptoms such as memory loss and confusion.
- Behavioral interventions: Behavioral interventions, such as cognitive training, may help improve cognitive function and reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- Lifestyle changes: Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy diet, and engaging in social activities may help slow the progression of Alzheimer's disease and improve quality of life.
Prevention of Alzheimer's Disease: While there is no guaranteed way to prevent Alzheimer's disease, there are several lifestyle changes that may help reduce the risk of developing the disease. These include:
- Regular exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity has been shown to reduce the risk of Alzheimer's disease.
- A healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats may help reduce the risk of Alzheimer's disease.
- Social engagement: Staying socially active may help reduce the risk of cognitive decline.
- Mental stimulation: Engaging in mentally stimulating activities, such as reading, playing games, or learning new skills, may help reduce the risk of cognitive decline.
Conclusion: Alzheimer's disease is a devastating disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. While there is no cure for the disease, there are treatments available that can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.